Temperatures are one of the main concerns for gamers, since they fear that their hardware will burn down in the short term and that their computer will no longer work properly overnight. To start with, when all computers are under load, it is normal for them to heat up, we say this because there are still people who find it unbelievable that a PC can get so hot.
The processor (CPU) and graphics card (GPU) are the components that tend to overheat the most because they are the primary sources of work when running games. RAM memories now come with built-in heat sinks, making it difficult to achieve high temperatures even when overclocked. It works almost the same way with motherboards, but in this case, the chipset is where the highest temperatures are reached; as a result, all motherboards have innovative heat sinks, and high-end cards even have their own fans integrated. Finally, storage units would only tend to get hot during data transfer, but even then, they hardly reach high-temperatures, and if they do, then the inside of your tower is not having good airflow, which is what we will talk about next.
Air Flow
To have a good airflow, you must consider the correct placement of fans as well as their position or direction; if the fans are in the wrong position, the hot air generated by the components inside will hardly leave the tower, accumulating heat, and your components will shoot up in temperature; this is very simple to understand, so the airflow should be as follows:
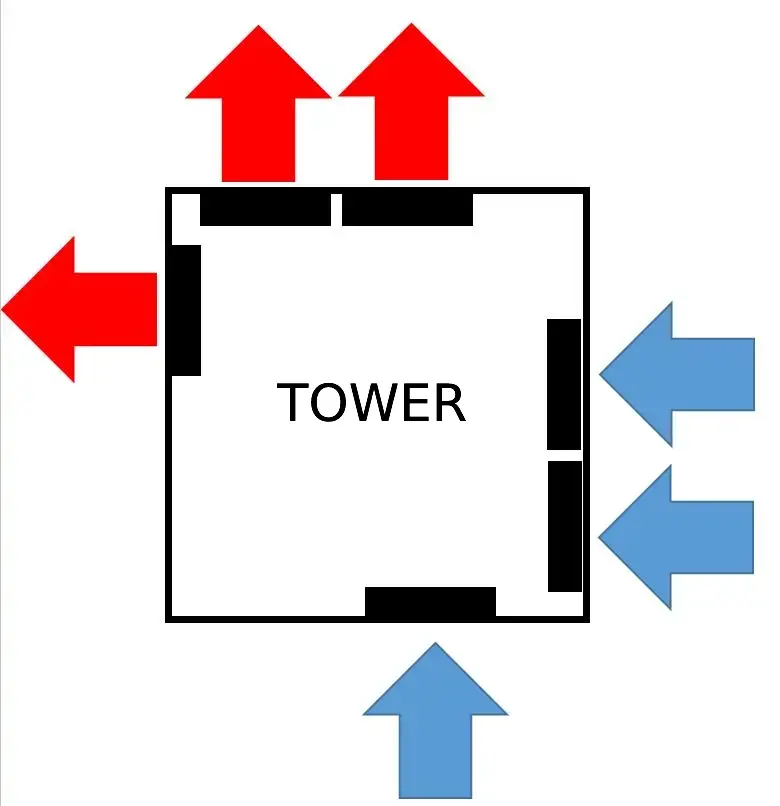
As illustrated in the image, the cool or cold air is drawn in by the front and bottom fans, and because hot air always tends to rise, the top and rear fans will pull the hot air out of the tower; this is how the correct air flow inside our tower should be, preventing our components from overheating. However, if you want this flow to be quick, making the hot air out as fast as possible and getting the components cooler, it is advisable to place fans at the top. Many people only install the rear fan missing out the top ones, which is also valid given that, as was previously mentioned, the hot air tends to rise and will nonetheless go out the top.
Now, knowing how the airflow inside the tower should be, what are the usual temperatures for the processor and graphics card when idle and under load? It should be made clear right away that this will be greatly affected by the environment the computer is in. The processor at rest is usually between 25 and 40 degrees Celsius, the graphics card is usually between 30 and 50 degrees Celsius, while under load, when you are playing a demanding video game for example, the processor is usually between 60 and 75 degrees Celsius and the graphics card between 60 to 75 degrees or even up to 80 degrees, these are very high temperatures for a human being, but the hardware can withstand it, if your graphics playing is between 70 to 80 degrees is normal and will not be damaged, but what happens if these temperatures are higher?

First of all, we should mention that processors, depending on the range and brand, indicate in their specifications that their maximum temperature is around 90, 95 or 100°C, and with graphics cards (GPU) it’s between 90 to 95°C. But this does not mean that you will be able to play at those temperatures without any issues, this only indicates that, if the CPU or GPU reaches its maximum temperature, the PC will automatically shut down to avoid any damage. Everything below 85°C is normal and safe for CPUs and graphics cards in general, but ideally, for extended gaming sessions, temperatures should be below 75°C or maximum 80°C for not so long sessions, so if your GPU is below 80°C, don’t worry, it’s normal. Therefore, it is often noted that temperatures between 80 and 85°C on your graphics card or CPU are still safe, but this should be treated as a warning sign that it is time for maintenance to decrease the temperatures and prevent them from rising in the future.
Can I damage my GPU if I play at temperatures exceeding 80°C?
As previously stated, GPUs have a fixed temperature limit; if the GPU hits that limit temperature, the computer will shut down immediately to prevent damage; this implies that the computer protects itself from high temperatures.
Your GPU will not catch fire or anything like that because that is how they are designed for, to withstand high temperatures under load, and if you play at more than 85°C it is very difficult to damage your GPU, but again, if you do not want your GPU to lower its performance or your computer to shut down, make sure that it does not exceed 85°C in temperature.

What can you do if your components are overheating?
First, dust will always accumulate inside the case because of the fans, and if this accumulates on the hardware, it will completely prevent the heat from dissipating, causing high temperatures. This is one of the main reasons that the temperatures of our components increase, so it is best to clean it from time to time or whenever you see dust accumulating, and the tools that can be used for this are as follows:
- Compressed air: A tool commonly used for computer equipment or systems; this is responsible for releasing high-pressure air to effectively remove dust from the hardware and is especially effective in hard-to-reach areas.
- Isopropyl alcohol: If dust remains stuck on the hardware for an extended period of time, even compressed air will not be able to remove it; this is where this type of alcohol is used; in theory, just spraying a little on the hardware and letting it dry would be sufficient, but in some cases it is necessary to carve it, with a brush that is not too scratchy, you put alcohol on it, and start cleaning with it, with this it will be easy to remove the dust adhered.
You may also like: How to split a Gaming PC between two or more people
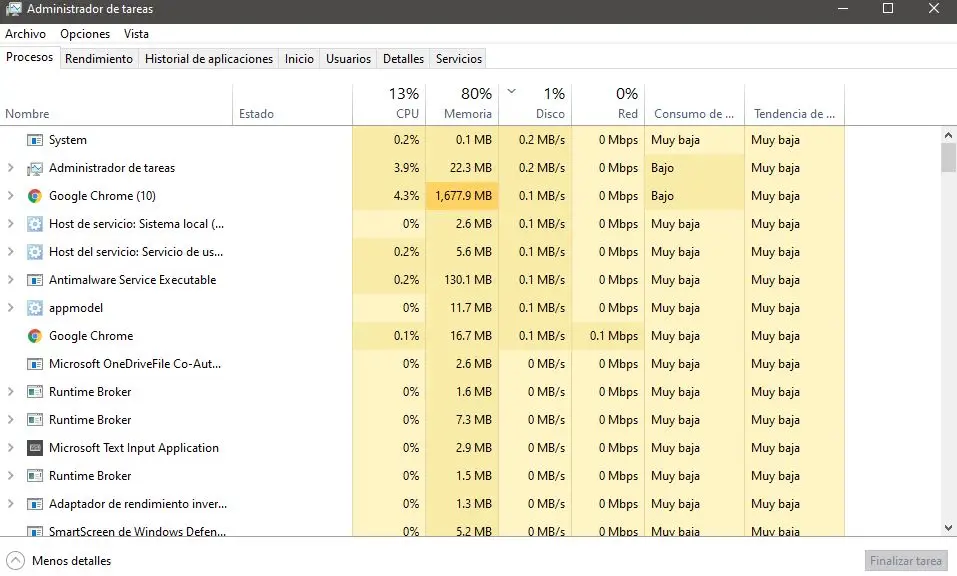
Whether high temps persist despite cleaning and dusting, see if a software isn’t using up PC resources, just by opening the task manager, right clicking on the taskbar > Task Manager or on your keyboard pressing CTRL + TAB + ESC, we can see all the processes running in real time, If you find an application utilizing a large percentage of the CPU or GPU, it is very likely that you have malware on your computer, therefore we will proceed to check it with Windows Defender antivirus. It is also highly suggested to download the free version of Malwarebytes, which is very effective in removing malware. If malware was successfully detected and removed, but there are still high temperatures or processes that use high percentages of CPU or GPU were not identified, proceed to the final option.
One of the most efficient ways to minimize high temperatures is to simply change the thermal paste; often, the thermal paste that comes with the heatsinks of CPUs and GPUs is of inferior quality. Both the CPU and the GPU may utilize the same thermal paste, but one is more difficult to apply.
What is thermal paste? Thermal paste is a thick substance that helps the heat sink make good contact with the processor making heat dissipation more effective. Without thermal paste, the processor would not cool at all.
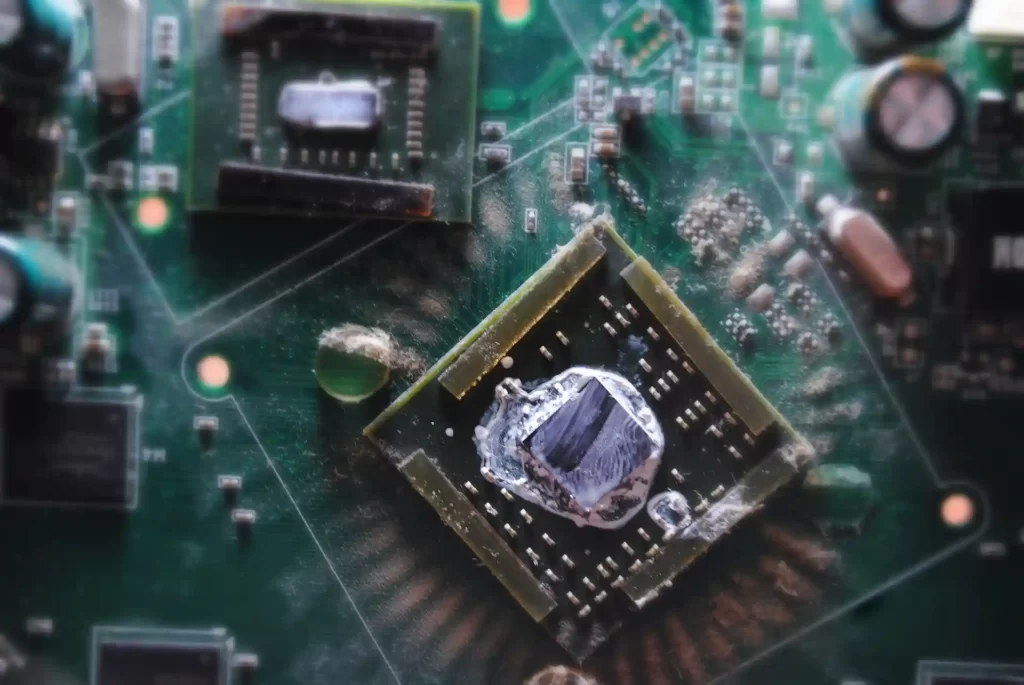
For our CPU, replacing the processor’s thermal paste is as easy as removing the heatsink, cleaning the dried paste on the heatsink and processor with isopropyl alcohol, and then restoring the heatsink with the new thermal paste. However, before changing the thermal paste, the following considerations should be made:
- Be sure to use the computer for some time before the thermal paste change: As is well known, the processor heats up, and when it is hot, it softens the thermal paste, making it very easy to remove the heatsink without too much effort. Otherwise, if the computer has not been used previously, the processor will be cold, and removing the heatsink will be very difficult, potentially causing damage to the processor or motherboard
- Be sure to use the correct amount of thermal paste: It is not good to use too much thermal paste, but it is also not good to use too little; the correct amount should be used so that it spreads around the processor when the heatsink is placed; if too much is used, it will spread too much until it comes out of the processor, making contact with the motherboard. If too little is utilized, it will not distribute evenly across the CPU, rendering the heatsink’s interaction with the processor inefficient for cooling.
The GPU is more complicated because it has to be taken apart piece by piece. This takes time because different graphics cards are built in different ways. If you’re not sure if you can do it, it’s best to have an expert take it apart and apply thermal paste. Another alternative is to configure a speed curve of the graphics card fans to make them more aggressive; this is done with software, the most popular of which is MSI Afterburner, which is compatible with almost all graphics cards; however, this program requires some knowledge, and it is advisable to find someone who knows how to handle the program to configure the speed of your fans; alternatively, you can search YouTube for how to make a custom curve; there are many tutorials explaining how to do so.